What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence (Ai) is the ability of a computer or system to mimic human-like intelligence processes. The more data you give AI, the more it becomes informed and up-to-date. These processes include learning, problem-solving, reasoning, perception, and language understanding.

Artificial intelligence generally has the following main components
1-Machine Learning
Machine learning is a branch of artificial intelligence that allows computers to learn based on data to perform specific tasks.
Basically, machine learning algorithms aim to recognize patterns, classify, make predictions, and automate various tasks based on data.
Basically, machine learning algorithms aim to recognize patterns, classify, make predictions, and automate various tasks based on data.
Some Basic Components and Categories of Machine Learning
Basic Components
1-Data
Machine learning relies on large amounts of data. The quality and quantity of data directly affects the success of the model.
2-Models
They are mathematical representations that learn from data and perform specific tasks. Different types of models are chosen for different problems.
3-Learning Algorithms
These algorithms are used to learn from data, such as regression, decision trees, support vector machines, and neural networks.

Categories
1-Supervised Learning
It is used in cases where correct answers (labels) are provided along with input data. The aim is to make predictions on new data by learning from the given data and labels. Example: Email spam filtering.
2-Unsupervised Learning
It tries to find structure and patterns among data without a labeled dataset. The goal is to understand data by grouping it or revealing its relationships. Example: Customer segmentation.
3-Reinforcement Learning
It allows an agent (i.e. a system) to learn by interacting with its environment. The agent improves its strategies with the feedback it receives (rewards or punishments). Example: Game-playing AI.
Application Areas
1-Health
Disease prediction and diagnosis
2-Finance
Credit risk analysis and fraud detection
3-Marketing
Customer behavior analysis and targeting
4-Automotive
Autonomous vehicles
Conclusion
Machine learning is a technology that has the potential to revolutionize many industries. Developing algorithms and increasing amounts of data allow machines to become smarter.
2-Natural Language Processing (NLP)
1-Tokenization
The process of breaking text into words or phrases.
2-Word Representations
Representation of words with mathematical vectors, for example, Word2Vec or Glove.
3-Part-of-Speech (POS) Tagging
Determining the functions of words in sentences (noun, verb, adjective, etc.).
4-Sentiment Analysis
Determining emotional tone in texts
5-Meaning Analysis
Techniques used to understand the meaning of words and expressions in context.
6-Machine Translation
The process of translating one language into another
Application Areas
1-Chatbots
Automated response systems used to interact with users.
2-Search Engines
Understanding user queries and providing feedback.
3-Text Classification
Classify emails as spam or normal.
4-Summarization
Making summaries of long texts.
5-Voice Assistants
Tools like Siri and Alexa understand user commands using natural language processing.
Technologies Used
1-Machine Learning
It is widely used in the field of NLP. Especially deep learning techniques achieve effective results on large text data.
2-Pre-Trained Models for Language Understanding
Models such as BERT, GPT, T5 show high performance in various NLP tasks.
Conclusion
Natural Language Processing is an important area for improving human-machine interaction and has revolutionary applications in many industries. Thanks to the development of NLP, we can communicate with our devices in a more natural way.
3-Image Processing
Image Processing is a technology that deals with the analysis, processing and interpretation of digital images. This field combines the fields of computer science, mathematics and engineering to extract and interpret information from images. Here are some of the basic components, methods and application areas of image processing:
Basic Components
1-Image Input
Transferring digital images to a computer. This can be photos, videos or other digital formats.

2-Image Processing Techniques
- Filtering
Applying mathematical operations on an image to reduce noise or highlight edges.
- Segmentation
Breaking the image into analyzable sub-parts.
- Attribute Extraction
Extraction of salient features or patterns (e.g., edge, shape, color) from an image.
3-Image Analysis
Interpreting the extracted features, giving them meaning and integrating them into decision-making processes when necessary.
Methods
1-Matlab and Python Libraries
The most popular software used for image processing include libraries such as OpenCV, PIL (Python Imaging Library) in Matlab and Python.
2-Machine Learning and Deep Learning
It is frequently used for image processing tasks. CNN (Convolutional Neural Networks) in particular are effective in classifying and analyzing images.
Application Areas
1-Medical Imaging
Analysis of medical images such as X-rays, MRIs and CT scans.
2-Image Recognition
Applications such as face recognition, object recognition.
3-Autonomous Vehicles
Image processing is used for vehicles to perceive their surroundings.
4-Agriculture
Monitoring agricultural lands and evaluating their condition
5- Digital Art
It is used in image editing and art creation processes.
Conclusion
Image Processing has an important place in many sectors and its application areas are constantly expanding with the development of technology.
4-Game Theory and Strategic Planning
Game Theory and Strategic Planning use mathematical and logical models to understand how individuals or groups respond to each other's behavior in decision-making processes. Game theory analyzes competitive and cooperative situations, while strategic planning determines how resources will be used to achieve goals. Here are the key elements of these two concepts and how they interact

What is Game Theory?
Game theory is a mathematical model that examines situations in which individuals (players) have a certain set of strategies, interact with each other, and outcomes are determined depending on these strategies.
Can be classified into two main types
1-Cooperative Games
These are situations where players come together to develop common strategies and share their gains. For example, two companies may collaborate on a project.
2-Competitive Games
Situations where players compete with each other and one player's gain is often associated with another's loss. For example, two firms may offer price cuts when competing in the same market.
Basic Concepts
1-Nash Equilibrium
It is a situation where each player does not change his strategy unless the other players change theirs. The fact that both parties prefer to stay at the same point means mutual dependency.
2-Dominant Strategy
It is a strategy that always provides a better result depending on the choices of other players.
3-Zero Sum Game
One player's gain is equal to another player's loss, so the total gain is always zero.
What is Strategic Planning?
Strategic planning is the process of determining the long-term goals of an organization, planning and implementing the steps necessary to achieve these goals.

Stages
1-Goal Setting
Defining the long-term goals that the organization wants to achieve.
2-Situation Analysis
Analysis of internal and external factors, determination of strengths and weaknesses. SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) is a frequently used method.
3-Strategy Development
Development of various strategies to achieve set goals. At this stage, game theory can help in predicting competitors' behavior and market dynamics.
4-Implementation and Monitoring
Implementation of planned strategies and continuous monitoring of results.
Examples and Applications
1-Marketing Strategies
Companies determine the most appropriate pricing by considering the pricing strategies of their competitors.
2-Political Games
Political candidates carefully analyze voters' preferences and their opponents' strategies.
3-Military Strategiesr
Countries should take into account the possible reactions of their rivals when planning their military actions.
Conclusion
Game Theory and Strategic Planning are powerful tools for understanding competitive and cooperative situations. By using these concepts, organizations can make more informed and effective decisions
Artificial Intelligence & Defense Industry
1-Defense Systems
Artificial intelligence is used in missile defense systems, cybersecurity, and threat detection systems. It increases the ability to detect and respond to threats.

2-Target Recognition and Tracking
Image processing and machine learning techniques enable rapid and accurate identification of targets. This is effectively used in land, air and sea operations.
3-Decision Support Systems
Artificial intelligence supports people in the strategic decision-making process. It helps to make more effective decisions by evaluating complex scenarios and making recommendations.
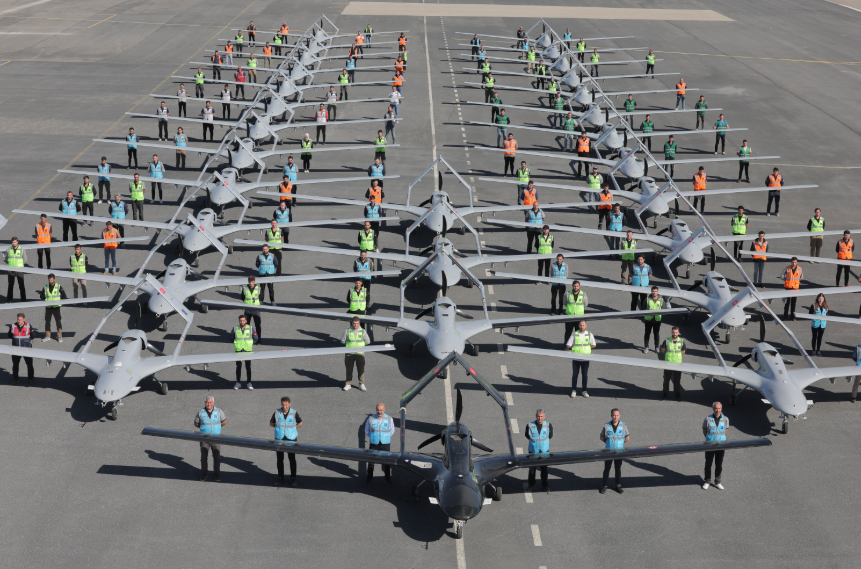

4-Autonomous Systems
Artificial intelligence plays a critical role in the development of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), unmanned sea vehicles, and autonomous land vehicles. These systems can operate without human intervention for tasks such as target detection, tracking, and attack.
5-Data Analytics
In the defense industry, big data analytics combined with artificial intelligence enables rapid processing and analysis of intelligence data. This helps predict enemy movements and make strategic decisions.
6-Simulation and Training
Artificial intelligence is used in the training of military personnel through simulations. It improves both individual and group training by creating realistic scenarios.

Conclusion
The role of artificial intelligence in the defense industry enables effective and safe military operations while also contributing to the development of new war strategies.
Data Traffic for Businesses
Data traffic in workplaces describes the information flow, data transfer and communication processes of an organization. This includes data exchange between employees, departments, systems and the external environment. Factors affecting data traffic for workplaces and points to consider in its management are as follows:

1. Types of Data Traffic
- Database Traffic
Queries to databases, updates and reporting processes.
- Network Traffic
Data transfer, file sharing and communication over the Internet and local network.
- Application Traffic
Data flow occurring within enterprise software (ERP, CRM, etc.).
2. Management of Data Traffic
- Bandwidth Analysis
Bandwidth, which affects the speed and throughput of data transfer, must be monitored and managed.
- Security
Data traffic should be encrypted and protected by firewalls.
- Redundancy
Backup strategies should be implemented to prevent data loss.
Effective management of data traffic is critical for the orderly and reliable operation of business processes.
Data Science
Data science is the process of extracting information from large data sets using statistical and mathematical methods. Data scientists analyze data, create models, and process the results. This process includes data collection, cleaning, analytical modeling, and visualization of results.
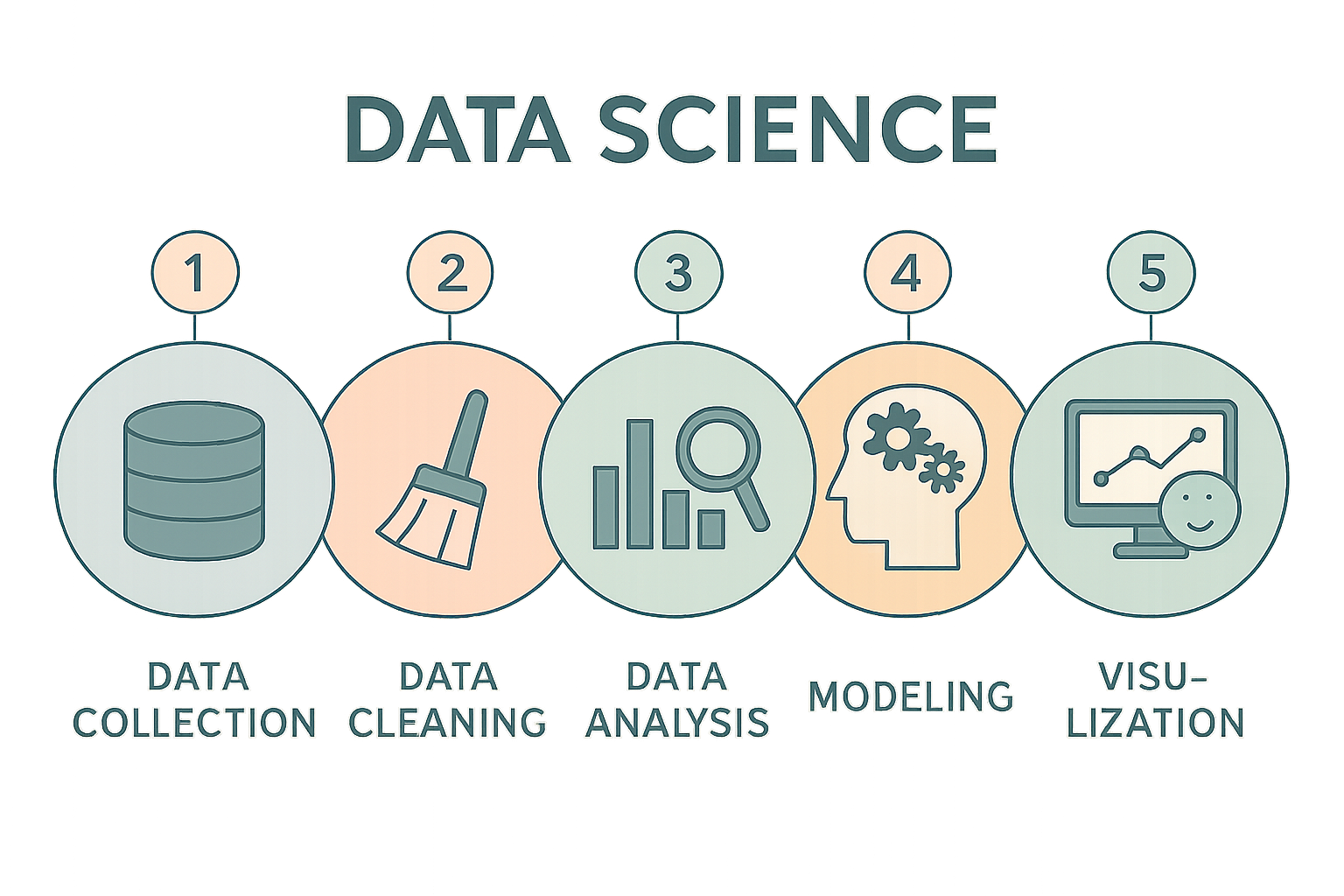
The key components of data science are
1-Data Collection
Collecting data involves obtaining it from specific sources or using existing data.
2-Data Cleaning
Correction of inaccurate or incomplete data to ensure data accuracy.
3-Data Analysis
Examination of data using statistical methods and algorithms.

4-Modeling
Application of machine learning algorithms to understand relationships and patterns in data.
5-Visualization
Presenting results and findings with graphs and tables.

Data science is used to support decision-making processes in various industries (healthcare, finance, marketing, etc.).
We Produce Data
All communication across platforms such as social media usage, messaging apps, and email creates data.
Data such as user behavior, click data, and interaction times are recorded.
Data such as user behavior, click data, and interaction times are recorded.
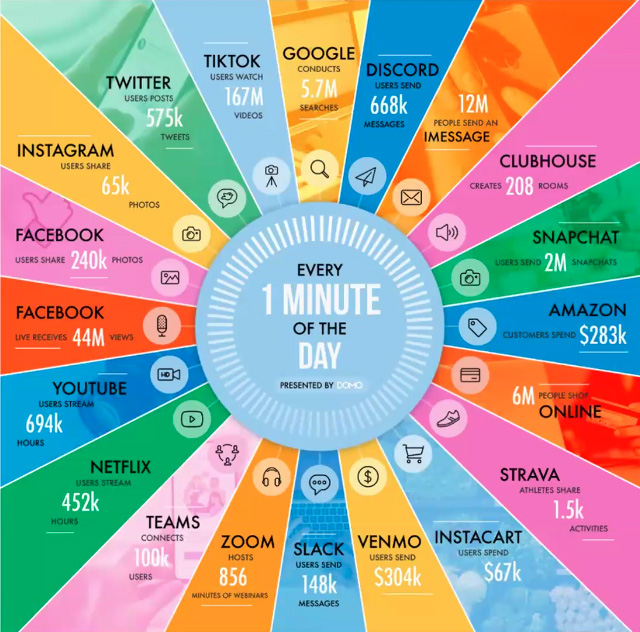
Surveys and Research
People share their thoughts, preferences and experiences by responding to surveys. This produces qualitative and quantitative data.

Sensor Data
Wearable technologies (smart watches, etc.) and mobile devices collect data such as physical activity, health data, and location information.
Shopping Behaviors
Records purchases made on online platforms, shopping history, and product reviews. This data is used to understand consumer behavior
Conclusion
The data produced in these ways can be analyzed and used to provide important insights, conduct scientific research, develop marketing strategies and many other areas.
